Tertiary education institutions – the sector at a glance
Universities
Section 268 of the Education and Training Act 2020 states that a university is "characterised by a wide diversity of teaching and research, … develops intellectual independence, and promotes community learning". The eight universities are:
- University of Auckland;
- Massey University;
- University of Canterbury;
- Lincoln University;
- University of Otago;
- Victoria University of Wellington;
- University of Waikato; and
- Auckland University of Technology.
Wānanga
Section 268 of the Education and Training Act 2020 states that a wānanga is "characterised by teaching and research that … assists the application of knowledge regarding ahuatanga Māori (Māori tradition) according to tikanga Māori (Māori custom)". The three wānanga are:
- Te Wānanga o Raukawa;
- Te Wānanga o Aotearoa Te Kuratini o Ngā Waka; and
- Te Whare Wānanga o Awanuiārangi.
Te Pūkenga and its Crown entity subsidiary companies
On 1 April 2020, the Government created a new tertiary education institution, Te Pūkenga – New Zealand Institute for Skills and Technology. On that day, the 16 institutes of technology and polytechnics became Crown entity subsidiary companies of Te Pūkenga.
There are currently 16 Crown entity subsidiary companies of Te Pūkenga. They are:
- Unitec New Zealand Limited;
- Otago Polytechnic Limited;
- Ara Institute of Canterbury Limited;
- Southern Institute of Technology Limited;
- Eastern Institute of Technology Limited;
- Western Institute of Technology at Taranaki Limited;
- Wellington Institute of Technology Limited;
- Waikato Institute of Technology Limited;
- Universal College of Learning Limited;
- Whitireia Community Polytechnic Limited;
- Manukau Institute of Technology Limited;
- The Open Polytechnic of New Zealand Limited;
- Nelson Marlborough Institute of Technology Limited;
- Tai Poutini Polytechnic Limited;
- Northland Polytechnic Limited; and
- Toi Ohomai Institute of Technology Limited.
As well as creating the 16 Crown entity subsidiaries, the legislative changes that came into effect on 1 April 2020 meant that industry training organisations became transitional industry training organisations.
At the end of 2021, Te Pūkenga set up an additional work-based subsidiary, named Te Pūkenga Work Based Learning Limited.
Figure 1
Main campus or headquarters of the tertiary education institutions in New Zealand
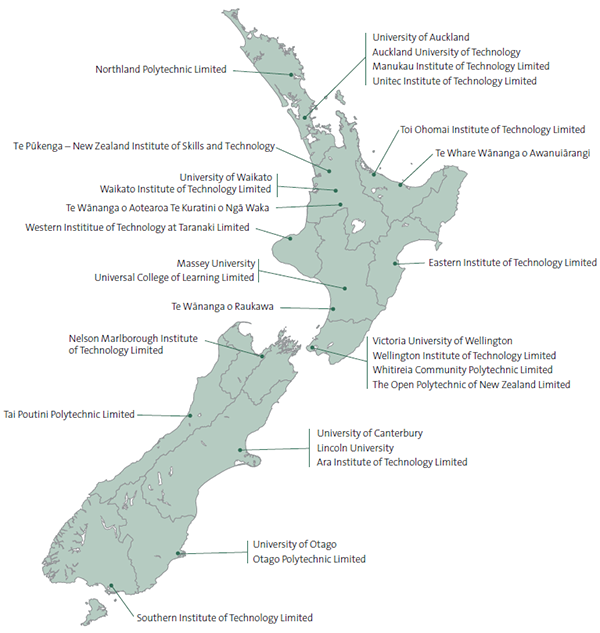
Figure 2
Total revenue, total assets, and total liabilities for 2020
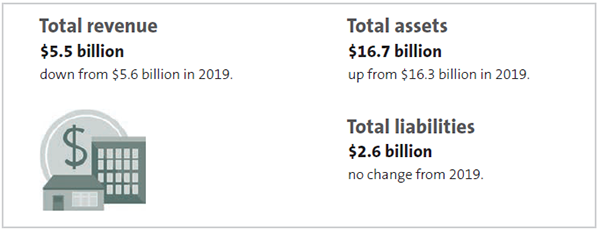
Source: Office of the Auditor-General.
Figure 3
Group surpluses and deficits, by type of tertiary education institution, 2016 to 2020
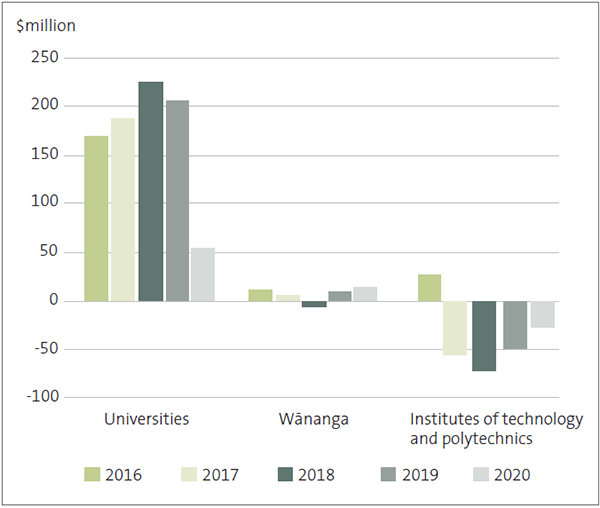
Source: Office of the Auditor-General.
Figure 4
Number of equivalent full-time students (EFTS)
Domestic students
| Tertiary education institution | 2019 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|
| Universities | 115,875 | 117,540 |
| Wānanga | 21,814 | 17,731 |
| Institutes of technology and polytechnics | 51,563 | 51,296 |
| Total | 189,252 | 186,567 |
International students
| Tertiary education institution | 2019 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|
| Universities | 21,042 | 18,780 |
| Wānanga | 15 | 12 |
| Institutes of technology and polytechnics | 10,870 | 9297 |
| Total | 31,927 | 28,089 |
Total equivalent full-time students
| Year | 2019 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|
| Total | 221,179 | 214,656 |
Source: Tertiary Education Commission, Single Data Return.1
1: The Single Data Return is a database of enrolment and completion information that the Ministry of Education and the Commission require certain tertiary education institutions to provide.